Endpoint Detection and Response, or EDR, is a form of technology that provides continuous monitoring and response to advanced cybersecurity threats against enterprise networks and systems. EDR is a subset of endpoint security, which takes a holistic approach to protecting corporate networks and data when employees access the network remotely via laptops, smartphones, and other mobile devices. Because these assets are at the end of the chain that connects a user to the company’s tech stack, they are referred to as endpoints.
Jump to:
- What’s the difference between endpoint security and EDR?
- What is endpoint detection and response?
- History of EDR
- How does endpoint detection and response work?
- Why is EDR important?
- Top EDR solutions
What’s the difference between endpoint security and EDR?
Endpoint security protects each endpoint on an enterprise network from vulnerabilities, hacking, and other cybersecurity threats. Endpoint security is responsible for ensuring the overall safety of endpoint devices and the corporate network.
Endpoint detection and response focuses specifically on frameworks used by security personnel to identify, investigate, and resolve advanced threats and sophisticated cyber attacks that are likely to compromise multiple endpoints.
What is endpoint detection and response (EDR)?
Endpoint detection and response is advanced threat awareness and prevention designed to mitigate the dangers that come from endpoint devices. EDR tools are designed to track endpoint diagnostics (logs, software downloads, possible malicious code) and provide detailed information that will help security teams identify, diagnose, and resolve security threats that compromise endpoint devices. These threats include:
- Using unprotected Wi-Fi networks, where attackers can spy on Internet sessions
- Losing a device or having it stolen
- Phishing campaigns and corresponding malware
- Weak passwords (or no password at all)
- Lack of control over company data
EDR goes a step further than endpoint protection, which is no longer enough for enterprise network protection: it’s proactive as well as defensive. EDR platforms remediate threats automatically and alert security administrators, who can perform manual remediation tasks and halt attacks as they’re occurring. These threats and attacks include misused credentials, database breaches, and ransomware.
Learn why free antivirus software won’t cut it for your company at TechnologyAdvice.com.
History of EDR
Endpoint detection and response is a comparatively new technology and topic in the IT world: The Internet wasn’t even available to enterprises until the 1990s. Security providers began offering endpoint-focused solutions in the 2000s. The term Endpoint Threat Detection and Response (ETDR) was coined in 2013 by a Gartner analyst, who wrote, “This name reflects the endpoint (as opposed to the network), threats (as opposed to just malware and officially declared incidents) and tools’ primary usage for both detection and incident response.” The term changed to EDR in 2015.
EDR meets a need that very quickly developed with the advent of endpoint-powered workforces: businesses suddenly required security for their systems and networks, which struggled against the barrage of cyberattacks that developed in the early 2000s. It is especially important for largely remote teams, which significantly increased during the COVID-19 pandemic.
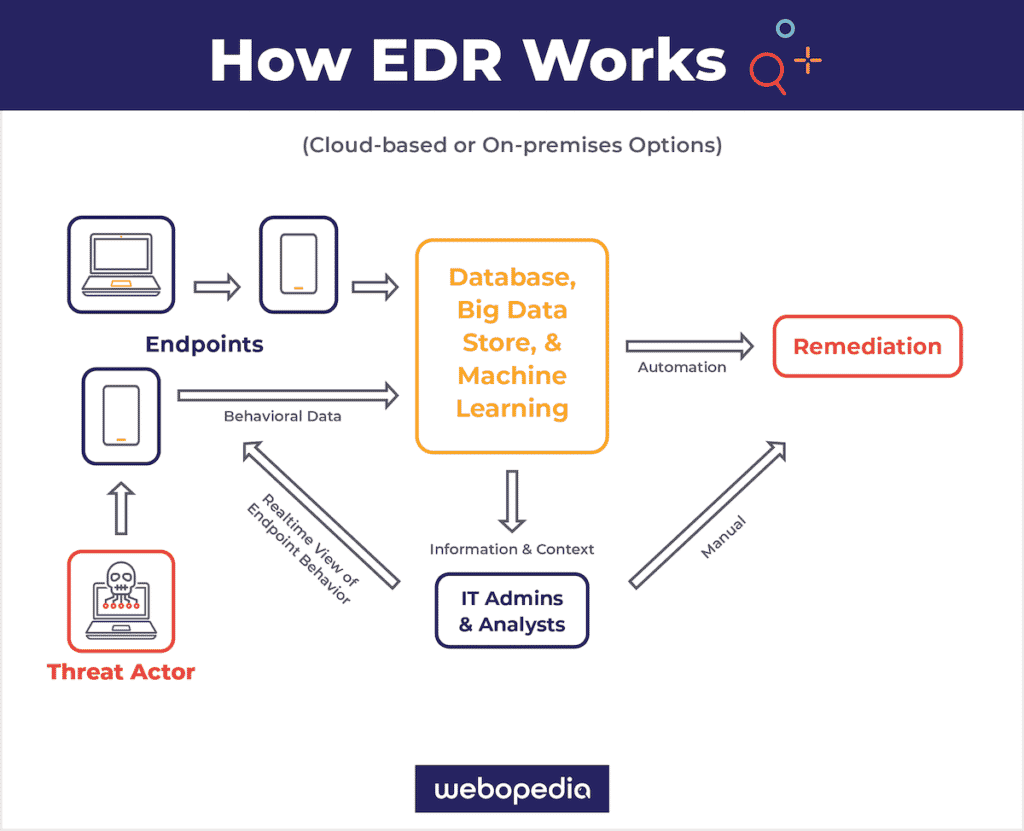
How does endpoint detection and response work?
Endpoint detection and response platforms perform these key functions:
- Collect endpoint and network data about traffic, disk and memory info, logins, and account activity
- Provide files and event logs for security teams
- Alert security operations centers (SOCs) and security analysts when the system detects anomalies or attacks
- Analyze the endpoint and network data collected so that enterprises can view patterns of both abnormal and normal traffic
- Perform remediation tasks, such as killing a process, blocking an application, or running a script to halt malicious behavior
- Allow security teams to look through files, event logs, network connection & configuration
A simplified day in the life of an EDR solution
- A threat actor, such as a strain of malware or ransomware, targets one of an enterprise’s endpoints.
- Endpoint data is collected and sent to the enterprise’s data lake or cloud database for analysis.
- Advanced big data analytics reveal an abnormal pattern in the day’s endpoint traffic.
- An alert is automatically sent to security or DevSecOps teams.
- The EDR platform does one of two things:
- Automatically remediates the threat.
- Allows security teams to handle the threat manually.
- The threat actor’s behavior is stored in the database so that the system remembers what the malicious pattern looked like and uses it to evaluate future threats.
Why is EDR important?
Current endpoint-based workforces require security that keeps up with sophisticated threats to networks and devices. EDR fills a hole in security approaches because it’s more than just prevention: the best EDR solutions provide the ability to halt an attack or mitigate its effects once it’s already occurring.
Endpoints are a major security risk to enterprises, as are the employees who use them. Not only do employees sometimes make poor password and device management choices, but they also present the greatest weakness in combating phishing attacks. EDR helps mitigate the high risk of compromised endpoint devices and networks by collecting important data and using it to halt attacks and breaches.
To clearly visualize EDR, watch Endpoint Detection And Response (EDR), Explained
Top endpoint detection and response tools
Popular Endpoint Detection and Response solutions include:
 Symantec Endpoint Protection is an add-on to Symantec products that provides incident investigation and response, intrusion prevention, anti-malware, and firewall features for servers and desktop computers. It also monitors endpoints and uses advanced machine learning (AML) to provide behavior analysis to identify suspicious activity. Other features include device and application control, kernel-level rootkit protection, role-based administration, group update provider, location awareness, policy-based settings, failover and load balancing, group update provider, the creation of additional global groups, enhanced LiveUpdate, and SQL database support. Deployments are typically organizations with more than 700 employees.
Symantec Endpoint Protection is an add-on to Symantec products that provides incident investigation and response, intrusion prevention, anti-malware, and firewall features for servers and desktop computers. It also monitors endpoints and uses advanced machine learning (AML) to provide behavior analysis to identify suspicious activity. Other features include device and application control, kernel-level rootkit protection, role-based administration, group update provider, location awareness, policy-based settings, failover and load balancing, group update provider, the creation of additional global groups, enhanced LiveUpdate, and SQL database support. Deployments are typically organizations with more than 700 employees.
 Cisco Advanced Malware Protection for Endpoints s a cloud-native solution to detect, contain, and remediate advanced threats across multi-domain control points. It includes threat hunting and integrated risk-based vulnerability management. The built-in SecureX platform features a unified view, simplified incident management, and automated response playbooks. The platform hunts proactively for threats and maps them to the MITRE ATT&CK framework. Licensing comes in three tiers, and the Premier tier includes human-led proactive threat hunting and high-fidelity alerts with recommendations for remediation.
Cisco Advanced Malware Protection for Endpoints s a cloud-native solution to detect, contain, and remediate advanced threats across multi-domain control points. It includes threat hunting and integrated risk-based vulnerability management. The built-in SecureX platform features a unified view, simplified incident management, and automated response playbooks. The platform hunts proactively for threats and maps them to the MITRE ATT&CK framework. Licensing comes in three tiers, and the Premier tier includes human-led proactive threat hunting and high-fidelity alerts with recommendations for remediation.
 Carbon Black Cb Response is designed for security operations center (SOC) teams. CB Response captures large amounts of information about endpoint events by performing unfiltered data collection. The data supports hunting threats in real-time and visualizing the entire attack kill chain. Aggregated threat intelligence is provided by the CB Predictive Security Cloud. CB Response is available through deployments including managed security service provider (MSSP), on-premises, virtual private cloud, and software as a service (SaaS). The company was founded by former members of the U.S. government’s team of offensive security hackers trained by the NSA and CIA.
Carbon Black Cb Response is designed for security operations center (SOC) teams. CB Response captures large amounts of information about endpoint events by performing unfiltered data collection. The data supports hunting threats in real-time and visualizing the entire attack kill chain. Aggregated threat intelligence is provided by the CB Predictive Security Cloud. CB Response is available through deployments including managed security service provider (MSSP), on-premises, virtual private cloud, and software as a service (SaaS). The company was founded by former members of the U.S. government’s team of offensive security hackers trained by the NSA and CIA.
 FireEye Endpoint Security employs techniques such as scanning for Indicators of Compromise (IoC), sandboxing, and retrospective analysis. Features include the ability to manage thousands of endpoint agents, threat detection across the whole organization, and a centralized management console. It also provides real-time, continuous endpoint monitoring, instant threat detection, detection automation, and rapid response to threats. FireEye Endpoint Security uses a single, small-footprint agent for minimal end-user impact and complies with regulations such as PCI-DSS and HIPAA.
FireEye Endpoint Security employs techniques such as scanning for Indicators of Compromise (IoC), sandboxing, and retrospective analysis. Features include the ability to manage thousands of endpoint agents, threat detection across the whole organization, and a centralized management console. It also provides real-time, continuous endpoint monitoring, instant threat detection, detection automation, and rapid response to threats. FireEye Endpoint Security uses a single, small-footprint agent for minimal end-user impact and complies with regulations such as PCI-DSS and HIPAA.
 CrowdStrike Falcon Insight provides endpoint security, threat intelligence, and cyberattack response services. Crowsdtrike’s Falcon cloud platform provides digital risk monitoring, antivirus, EDR, XDR, NGAV, managed threat hunting, vulnerability assessment, threat intelligence, automated malware analysis, and cloud and container security, and cloud workload protection. Crowdstrike appeals to companies of different sizes and needs with their Falcon Pro, Enterprise, Premium, and Complete tiers of service and provides breach protection for platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. Crowdstrike was also involved in the investigations of several high-profile commercial and international cyberattacks.
CrowdStrike Falcon Insight provides endpoint security, threat intelligence, and cyberattack response services. Crowsdtrike’s Falcon cloud platform provides digital risk monitoring, antivirus, EDR, XDR, NGAV, managed threat hunting, vulnerability assessment, threat intelligence, automated malware analysis, and cloud and container security, and cloud workload protection. Crowdstrike appeals to companies of different sizes and needs with their Falcon Pro, Enterprise, Premium, and Complete tiers of service and provides breach protection for platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. Crowdstrike was also involved in the investigations of several high-profile commercial and international cyberattacks.
 McAfee MVISION is an agentless cloud access security broker (CASB) that puts itself between cloud service users and cloud applications to monitor, investigate, and respond to threats. It uses user entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to identify threats; provides API integration to cloud services for real-time control over user access, collaboration, data, and shadow IT and personal device access; and continuously audits infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) environments. The product offers threat protection and data loss prevention to large and very large enterprises of more than 1,000 employees. It also offers specialized features such as a dedicated GDPR tool for companies affected by the law.
McAfee MVISION is an agentless cloud access security broker (CASB) that puts itself between cloud service users and cloud applications to monitor, investigate, and respond to threats. It uses user entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to identify threats; provides API integration to cloud services for real-time control over user access, collaboration, data, and shadow IT and personal device access; and continuously audits infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) environments. The product offers threat protection and data loss prevention to large and very large enterprises of more than 1,000 employees. It also offers specialized features such as a dedicated GDPR tool for companies affected by the law.
 RSA NetWitness Endpoint continuously monitors desktop computers, servers, and virtual machines to provide threat visibility at organizations’ endpoints. Threat intelligence utilizes a behavioral-based analytics engine and machine learning. Other features and methods include live memory analysis, whitelisting and blacklisting, certificate validation, endpoint baselining, and customized rulesets, and it does not require signatures or rules. Threat intelligence is provided by RSA, the RSA NetWitness Suite community, and third parties. The tool aligns with industry standards from NIST, US-CERT, SANS, and VERIS, and it uses FIPS-compliant encryption, and the top five industries served are financial, government, healthcare, energy, and telecommunications.
RSA NetWitness Endpoint continuously monitors desktop computers, servers, and virtual machines to provide threat visibility at organizations’ endpoints. Threat intelligence utilizes a behavioral-based analytics engine and machine learning. Other features and methods include live memory analysis, whitelisting and blacklisting, certificate validation, endpoint baselining, and customized rulesets, and it does not require signatures or rules. Threat intelligence is provided by RSA, the RSA NetWitness Suite community, and third parties. The tool aligns with industry standards from NIST, US-CERT, SANS, and VERIS, and it uses FIPS-compliant encryption, and the top five industries served are financial, government, healthcare, energy, and telecommunications.
 SentinelOne is an advanced, enterprise-scale tool that combines EDR and endpoint protection platform (EPP) capabilities to protect the entire enterprise and cloud attack surface. It operates not just across endpoints, but all other aspects of a network, including containers, cloud workloads, and internet of things (IoT) devices. SentinelOne provides threat identification and blocking with its own patented behavioral and static AI models. It provides a centralized console for managing assets and discovering and controlling devices. Detection and response includes fileless, zero-day, and nation-grade attacks.
SentinelOne is an advanced, enterprise-scale tool that combines EDR and endpoint protection platform (EPP) capabilities to protect the entire enterprise and cloud attack surface. It operates not just across endpoints, but all other aspects of a network, including containers, cloud workloads, and internet of things (IoT) devices. SentinelOne provides threat identification and blocking with its own patented behavioral and static AI models. It provides a centralized console for managing assets and discovering and controlling devices. Detection and response includes fileless, zero-day, and nation-grade attacks.
 RAPID7 provides tools to enterprises to assess their attack surface, detect suspicious behavior early on, and to rapidly respond to threats and remediate. Their Insight Platform simplifies EDR across local, remote, cloud, containerized, and virtual environments. The platform provides threat intelligence, vulnerability and risk management, application security, and security automation through a unified cloud-SIEM and XDR approach. RAPID7 is also known for its collaboration with the open-source community to produce Metasploit, a widely-used penetration testing framework.
RAPID7 provides tools to enterprises to assess their attack surface, detect suspicious behavior early on, and to rapidly respond to threats and remediate. Their Insight Platform simplifies EDR across local, remote, cloud, containerized, and virtual environments. The platform provides threat intelligence, vulnerability and risk management, application security, and security automation through a unified cloud-SIEM and XDR approach. RAPID7 is also known for its collaboration with the open-source community to produce Metasploit, a widely-used penetration testing framework.
 Cynet offers enterprises security loophole identification, threat intelligence, and managed endpoint security. The Cynet Autonomous Breach Detection platform combines XDR, response automation, and MDR services into one comprehensive service. The platform unifies NGAV, EDR, network detection rules, UBA rules, and deception technology. Automations include root cause investigation, comprehensive threat responses, remediation, and reporting. Their CyOps managed services provide alert monitoring, proactive threat hunting, detailed attack analysis, and expert remote assistance with containing and eliminating threats. The company is also known for discovering major vulnerabilities in consumer electronics affecting millions of devices.
Cynet offers enterprises security loophole identification, threat intelligence, and managed endpoint security. The Cynet Autonomous Breach Detection platform combines XDR, response automation, and MDR services into one comprehensive service. The platform unifies NGAV, EDR, network detection rules, UBA rules, and deception technology. Automations include root cause investigation, comprehensive threat responses, remediation, and reporting. Their CyOps managed services provide alert monitoring, proactive threat hunting, detailed attack analysis, and expert remote assistance with containing and eliminating threats. The company is also known for discovering major vulnerabilities in consumer electronics affecting millions of devices.
Read more about enterprise EDR tools: Top Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) Solutions
This article was updated October 2021 by Jenna Phipps, and in March 2022 by Lucas Ledbetter.

