A list of many common broadband wired and wireless router settings and a description of what function it performs.
A router is a device that forwards data packets along networks. It connected to at least two networks, commonly two LANs or WANs or a LAN and its ISP’s network.
For most home users, they may want to set-up a LAN (Local Area Network) or WLAN (Wireless LAN) and connect all computers
to the Internet without having to pay a full broadband subscription service to their ISP for each computer on the network. In many instances, an ISP will allow you to use a router and connect multiple computers to a single Internet connection although some providers do charge a fee for each additional computer sharing the connection. This is when you’ll want to look at smaller routers, often called broadband routers that enable two or more computers to share an Internet connection.
Finding the IP address for your Router
Your router IP is determined by the brand of router you use. For example Linksys routers use 192.168.1.1, while D-Link routers usually use 192.168.0.1. The documentation that comes with your router will provide your router IP address, however if you can’t find your manual you can find the IP address using ipconfig.
- Type cmd in the search or run box from your Windows Start Menu.
- When the command window opens type: ipconfig and hit enter.
- This will show your local network information. The IP address listed as Default Gateway is your router’s IP.
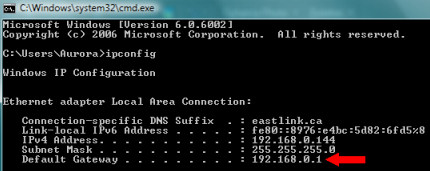
When you type that address in to your browser, for example, you can then log in to the router to access settings.
Common Router Settings
Here is a list of many common broadband wired and wireless router settings and a description of what function it performs. It is important to remember that the exact names of different settings and options will differ, depending on your router manufacturer and the device’s firmware. However, most will have similar settings and options.
Access Control |
These options let you to control access, both in and out of your network. Access Control let you do things like grant access to approved Web sites, limit Web access, or even block Internet access for some applications such as Peer-to-peer file sharing or Internet gaming applications. |
Application Rules |
Application rules are used to open single or multiple ports on your router when the router senses data sent to the Internet on a “trigger” port or port range. |
Auto Channel / Channel Scan |
This option will enable the router to scan and find the channel with least interference and then use that channel for wireless networking. (see Wireless Channel below) |
DHCP Server Settings |
Short for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, the DHCP section is where you can configure the router’s built-in DHCP Server to assign IP addresses to the computers and other devices on your local area network (LAN). Other DHCP options include Enable DHCP Server and Add or Edit DHCP Reservation. |
DMZ |
Short for demilitarized zone, the setting DMZ options allow you to expose a computer on your network to the Internet for use of a special-purpose service, like online gaming, VPN access, or videoconferencing. |
DNS |
DNS (Domain Name System ). If you don’t know it, your ISP can provide you with at least one DNS to enter in this setting. |
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) |
Dynamic DNS, or DDNS is a setting lets you host a server, such as a Web server, FTP server or game server) using a domain name that you have purchased. |
Enable Wireless |
This setting is used to turn on and off the wireless connection feature of your router. |
Firewall Settings |
A firewall is a system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. This router setting is used to set a single computer on your network outside of the router. |
Firmware / Firmware Version |
This is the version of firmware used by your router. From this section in your settings you can also download firmware updates from the maufacturer. |
Gateway |
The gateway address is your ISP server’s IP address. If you do not know it, your ISP can provide it. |
Inbound Filter(s) |
Inbound Filters are used to limit access to a server on your own network. Filter rules can be used with Virtual Server, Port Forwarding, or Remote Administration features. |
Internet IP |
This is your Router’s IP address, when seen from the Internet. This address can be obtained from your own ISP |
MAC Address |
A unique ID assigned by the manufacturer of the network adapter (see MAC address). |
MAC Address Filter |
Short for Media Access Controller (MAC) filter, is used to control network access based on the MAC Address of the network adapter. The MAV address filter is used to allow or deny network or Internet access. |
Max Idle Time |
The Max Idle Time can be set to terminate the Internet connection after it has been inactive for a specified period of time, called the Max Idle Time |
MTU |
MTU is short for Maximum Transmission Unit. Here you can specify the largest packet size permitted for Internet transmission. An “auto” MTU option lets the router to select the best MTU for your Internet connection |
Port Forwarding |
This option is used to open multiple ports (or a range of ports) in your router and redirect data through those ports to a single PC on your network. |
PPPoE |
Short for Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet, this option only needs to be used if your ISP requires you to use a PPPoE. |
Pre-Shared Key |
You can set a key as a pass-phrase of up to 63 alphanumeric characters. It cannot be shorter than eight characters. |
Subnet Mask |
This is the Router’s Subnet Mask, as it is seen by users on the Internet. If you do not know it, your ISP can provide it. |
System Logs |
This is where you access your router logs to view events. |
Text (for) Banner |
A “text banner” is a message that is displayed when someone logs in to the router. Text banners usually include a message to indicate that unauthorized access is prohibited. |
Visibility (Wireless) Status |
This setting lets you show or hide your wireless network. To hide the wireless network use the invisible option. In visible mode the network name is broadcast to anyone within the range of your signal. |
Website Filter |
The Web Filter option allows you to set up a list of allowed Web sites that can be used by multiple users, and any site not listed here will be blocked. |
WEP |
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a wireless encryption method. WEP is not as secure as WPA encryption. |
Wireless Channel |
You can manually choose the clearest channel to help optimize the performance and coverage of your wireless network (see above Auto Channel Scan). |
Wireless Network Name |
This is the name that will appear in the list when you browse for wireless networks (unless visibility is set to Invisible). Users should change the pre-configured network name. |
WPA |
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) uses a variant of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) security standards published by the Wi-Fi Alliance. |
WPA Mode |
This option can be used if the clients to be used with the router only support the older standard. |
This article was originally published on November 21, 2008

