Network Topology refers to layout of a network. How different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate is determined by the network’s topology.
 Network Topology refers to the layout of a network and how different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate. Topologies are either physical (the physical layout of devices on a network) or logical (the way that the signals act on the network media, or the way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next). This Webopedia Study Guide describes five of the most common network topologies.
Network Topology refers to the layout of a network and how different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate. Topologies are either physical (the physical layout of devices on a network) or logical (the way that the signals act on the network media, or the way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next). This Webopedia Study Guide describes five of the most common network topologies.
Network Topology Checklist
Getting Started: Key Terms to Know
The following definitions will help you to better understand network topology:
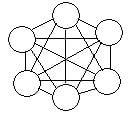
1. Mesh Topology
Mesh Topology: In a mesh network, devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes. In a true mesh topology every node has a connection to every other node in the network. There are two types of mesh topologies:
2. Star Topology
Star Topology: In a star network devices are connected to a central computer, called a hub. Nodes communicate across the network by passing data through the hub.

3. Bus Topology
4. Ring Topology

Ring Topology: A local-area network (LAN) whose topology is a ring. That is, all of the nodes are connected in a closed loop. Messages travel around the ring, with each node reading those messages addressed to it.
Main Advantage: One main advantage to a ring network is that it can span larger distances than other types of networks, such as bus networks, because each node regenerates messages as they pass through it.
5. Tree Topology
Tree Topology: This is a “hybrid” topology that combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. In a tree network, groups of star-configured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone cable.
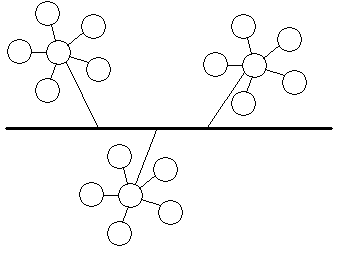
Main Advantage: A Tree topology is a good choice for large computer networks as the tree topology “divides” the whole network into parts that are more easily manageable.
Main Disadvantage: The entire network depends on a central hub and a failure of the central hub can cripple the whole network.
This article was last updated on May 13, 2019