Virtual Machine

A virtual machine (VM) is an isolated, digital instance of a computer—its operating system, applications, and memory— without the underlying hardware that allows organizations to scale compute power, test malware, and develop software.
Virtualization turns conventional physical computers into hosts for multiple virtual computers. Amidst trends like increasing global reliance on digital technology, virtual machines efficiently maximize existing physical devices. Since the late 1990s, virtualization – and its spinoff, containerization – has been a critical innovation in software development.
In this definition...
Why Use A Virtual Machine?
Blank Canvas
Through virtualization, users can deploy different types of operating systems and OS-specific programs from the host OS enabling legacy app usage, code development, and more.
Sandbox Environment
Virtual machines are isolated environments giving analysts a space for testing software and suspicious malware without risking security breaches or disruption of the production environment.
DevOps Optimization
Virtualization offers scalability and efficiency for deploying complex applications and software for the digital economy through development-friendly methods.
How Do Virtual Machines Work?
Virtual machines typically get implemented via a hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine manager (VMM), within virtualization types. Hypervisors can be embedded hardware or software or installed separately to implement virtualization on the host device.
Hypervisors serve as an intermediary between hardware and software, creating a unique instance that a user can manage as an isolated environment within the physical host.
Virtual Machine Features
- Capacity: Running virtual machines enables scaling of processing power and storage without the physical infrastructure
- Diversification: Installing a unique operating system on a VM for a given project
- Legacy: Running legacy applications to use or access discontinued programs and data
- Snapshots: Saving system-level progress points for the VM establishing replication
- Sandbox: functionality as an isolated environment for testing suspicious programs
- Exploration: tinkering with different system tools for educational purposes
- Sharing: packaged to share for collaboration and deployment with stakeholders
Check out the Best Server Virtualization Software of the year.
Types of Virtual Machines
Process Virtual Machines
Also known as a managed runtime environment – like Java Runtime Environment (JRE) – these VMs mimic the behavior of computers (simulation) and run a single program or process. Other examples include Java Virtual Machine (JVM), Parrot Virtual Machine (PVM), and Common Language Runtime (CLR).
System Virtual Machines
Also known as hardware VMs, system virtual machines duplicate computer behavior (emulation) with full computer operating system access. Examples include VMware, VirtualBox, Windows, Virtual PC, and Citrix Xen.
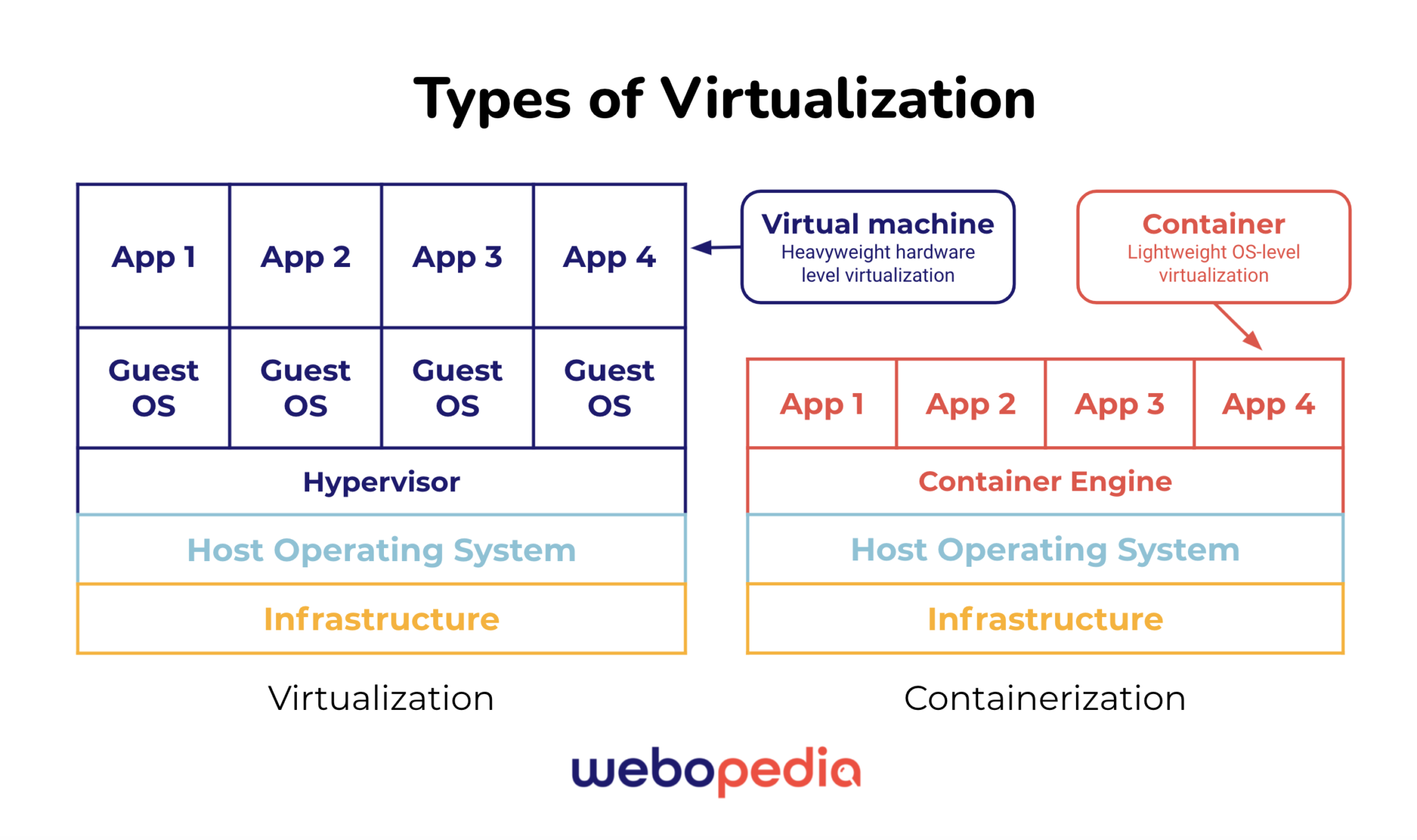
Virtual Machines vs. Containers
Virtual machines and containers are examples of virtualized environments, but they differ in their features and size. Virtual machines are the traditional virtualization method and usually allow a computer to run a few, large VMs.
Containers, by comparison, are becoming a popular method for deploying microservices with far more containers fitting onto a single host. Whereas VMs use a hypervisor to create virtual instances, containers use a container engine like Docker.
Read more about securing virtual systems with Cloud Security for Virtual Machines and Containers on ServerWatch.
Virtual Machine Vendors
- HPE
- IBM
- Microsoft
- Oracle
- Red Hat
- VMware
Updated by Sam Ingalls on August 24, 2021.

