A programming language is a vocabulary and set of grammatical rules for instructing a computer or computing device to perform specific tasks. The term programming language usually refers to high-level languages, such as BASIC, C, C++, COBOL, Java, FORTRAN, Ada, and Pascal.
How does programming language work?
Each programming language has a unique set of keywords (words that it understands) and a special syntax for organizing program instructions.
A program written in a particular programming language has two parts: instructions written in that language and statements written in another language called machine code. Machine code is a binary format that consists of ones and zeros (1 and 0); each digit represents either an instruction or data within the program.
When a programmer types a command into their computer’s terminal, it sends those instructions to their computer’s processor, which translates them into machine code, so it can execute them. It then takes any information produced by those commands and translates it back into something humans can understand—usually English.
The process is similar for websites; when a user enters text into a search engine like Google, it converts the user’s query into machine code before sending it off to its servers. It then processes all of the results from its search algorithm using machine code before translating them back into a human-readable form.
To learn more about programming, check out these courses.
TechRepublic Academy
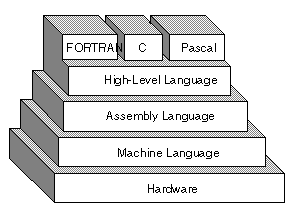
High-Level Programming Languages
High-level programming languages, while simple compared to human languages, are more complex than the languages the computer actually understands, called machine languages. Each different type of CPU has its own unique machine language.
Lying between machine languages and high-level languages are languages called assembly languages. Assembly languages are similar to machine languages, but they are much easier to program in because they allow a programmer to substitute names for numbers. Machine languages consist of numbers only.
Lying above high-level languages are languages called fourth-generation languages (usually abbreviated 4GL). 4GLs are far removed from machine languages and represent the class of computer languages closest to human languages. Regardless of what language is used, the program must eventually be converted into machine language so that the computer can understand it. There are two ways to do this:
1) Compile the program.
2) Interpret the program.
Recommended Reading: See compile and interpreter for more information about these two methods.
What are a programming language’s key functions?
The main functions of a programming language are to store and manipulate data, control hardware, provide security, and be an understandable medium for humans. Most programming languages share these functions as their key characteristics but differ in many ways, such as syntax or library sizes.
Other functions vary based on how they’re being used. For example, if a language is being used to control hardware, it needs additional programs that tell it how to process data without human interaction.
In addition, encryption may be needed if it’s used for communications between two devices. Programming languages use standardized functions to communicate with each other, so compatible devices can communicate.
Who uses programming languages?
Anyone who writes computer programs will use a programming language. Programmers are in charge of translating people’s ideas into code, from video games to websites to software. They write documentation about how to write code for an application or website. Some professionals that use programming languages include:
- A software or application developer creates applications for computers and mobile devices using languages like Java, C++, or Objective C.
- A computer systems analyst uses programming languages to develop new technologies and create better ways for businesses to run. These individuals study business processes, workflow processes, and user needs to design new technologies to help enterprises operate more efficiently.
- A web developer is someone who builds websites. Web development has many specialities (e.g., front-end development, back-end development). Generally speaking, web developers build both client-side and server-side applications using languages like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, Ruby on Rails, or other programming languages depending on the project requirements.
- A computer systems engineer plays an important role in programming software and overseeing networks, systems, computers, and telecommunications devices. They also write computer programs to debug software problems. These engineers typically work as part of large teams, including hardware engineers, network engineers, and software engineers.
- An application developer turns an idea into a product by writing code for a specific platform (like iOS or Android) using languages like Swift or Java.
Types of programming languages
There are many different programming languages in use today, but they fall into five main categories according to their purpose. They include:
Procedural Programming Language
A procedural programming language uses statements to specify actions, allowing a programmer to write instructions (called procedures) a computer can execute. These instructions tell a computer what operations to perform on given data and how these operations should be performed.
Functional Programming Language
A functional programming language emphasizes functions that return values, which can be used by other functions or be assigned as values to variables or data structures. It treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids state and mutable data. Functional languages were designed with theorem-proving in mind rather than traditional computer applications.
Scripting Programming Language
A scripting programming language supports scripts—programs written for a special run-time environment that automate tasks normally performed by humans—as opposed to standalone programs.
Logic Programming Language
A logic programming language allows programmers to write programs based on rules expressed in logical form.
Object-Oriented Programming Language
An object-oriented programming language supports object-oriented analysis and design (OOA&D). It has become increasingly popular since the mid-1980s and is now almost universally supported in modern programming languages.
What is the top programming langauge?
According to IEEE Spectrum’s interactive ranking, Python is the top programming language of 2017, followed by C, Java and C++. Of course, the choice of which language to use depends on the type of computer the program is to run on, what sort of program it is, and the expertise of the programmer.

Source: Github Octoverse
JavaScript is the most common programming language according to GitHub Octoverse in 2021. However, the best language depends on the programmer’s use cases. JavaScript, Python, Java, PHP, C++, Ruby, and other programming languages are used in various ways depending on the programmer’s needs.
When it comes to choosing a programming language, there’s no single right answer. Each one has its own strengths and weaknesses—and those change over time as new versions of languages are released.
The important thing is to understand a project’s programming language requirements before deciding which one is best for the project.
Five most common programming languages
Five most common programming langauges because no programming language is strictly superior, it’s best to choose one that fits a programmer’s project’s use case. Here are the most common programming languages.
Javascript
JavaScript is a lightweight programming language that runs in web browsers. It’s a scripting language for both client-side (web-based) and server-side (running on web servers) uses.
It enables websites to store and use data, access parts of pages known as components, update those components’ contents, run functions when events happen on a website, make pages more interactive, etc.
Moreover, it’s supported by all major browsers, which means it can reach virtually any user across multiple platforms (Windows PCs, Macs, Linux computers). In short, JavaScript is arguably one of the most important programming languages in today’s age of web development.
Common JavaScript use cases
The most common use of JavaScript is to create interactive elements on web pages, such as user login boxes, checkboxes, or dropdown menus that all become active when users hover over them with their mouse pointer.
It’s often used in conjunction with other markup languages such as HTML and stylesheet languages such as CSS as part of an overall website design and development process. Other JavaScript use cases include:
- Interactive website design
- Game development
- Application development
- Web and mobile app development
Python
Python is a simple language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991. It is an interpreted language, meaning it doesn’t need to be compiled before use.
Python offers a wide range of features, including support for multiple programming paradigms (imperative, object-oriented, etc.), exception handling (try/except/finally), dynamic typing (dynamic type checking), a very small runtime environment with fewer dependencies than other languages, full Unicode support, and much more.
Common Python use cases
Python is an interpreted high-level programming language for general-purpose programming. It can be used to automate tasks, conduct data analysis, create graphical user interfaces (GUIs), develop video games, and more. Other Python use cases include:
- Data visualization and data science
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and subsets such as big data, data analytics, etc.
- Development of web scraping applications
Java
Java is both a programming language and a computing platform. Programmers can use Java to write apps for phones, desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and smartwatches. And because it is based on C/C++ syntax, many of its commands are similar.
But where C/C++ enables developers to write low-level code for systems programming, Java was designed for high-level app development.
It was initiated in June 1991 by James Gosling, Mike Sheridan, Chris Warth, Ed Frank, and Patrick Naughton. However, it was initially released at Sun Microsystems in 1996 after undergoing different name iterations (Oak, Green, and Java from Java coffee).
Common Java use cases
Java is a programming language that allows programmers to build applications and software. Thanks to its object-oriented nature, a massive library of prebuilt APIs, and cross-platform capabilities, it’s especially useful for creating enterprise apps.
Java can create anything from games to mobile apps, desktop applications, websites, enterprise software, and embedded systems. Other use cases include:
- Building financial sector server apps, such as thos that run ATMs
- Developing desktop GUI applications
- Scientific applications, such as MATLAB
- Building software tools, such as NetBeans IDE
TypeScript
TypeScript is an open-source, object-oriented language developed and maintained by Microsoft. This JavaScript superset adds types, classes, and modules to JavaScript and allows developers to write applications on any browser or platform without additional compiling.
It’s used in large-scale web applications and popular libraries such as AngularJS. In addition, TypeScript is based on ECMAScript 6th Edition (ES6), so it’s highly compatible with most other JavaScript codebases.
Common TypeScript use cases
TypeScript’s purpose is to simplify large-scale applications through advanced features such as optional static types, classes, and modules. Many organizations that employ TypeScript also use it for microservices—small pieces of code built to perform a single task—as it improves unit testing.
TypeScript also helps reduce bugs, streamline programming processes, enhance code readability, and implement tooling support.
C#
C# (C Sharp) is an object-oriented programming language that Microsoft developed within its .NET initiative. The language is a hybrid of C and C++ that encompasses strong typing, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines.
Common C# use cases
C# is a modern programming language used for building applications for web, desktop, mobile, gaming platforms, and embedded devices. It’s most commonly associated with Windows development but is also popular with Microsoft’s Xamarin for mobile development and Android apps.
Further, C# can be used for game development, web app development, and Windows application development.



